Pricing
From Business Model Canvas to Pricing Model Canvas
Home / Blog / From Business Model Canvas to Pricing Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas has become the standard for business model development. However, to be successful and, above all, profitable, you also need a Pricing Model Canvas—reason enough for Prof. Roll & Pastuch to create/develop such a framework. The framework is useful to quickly gain an overview of the most important topics in pricing and to avoid getting lost in the details in the first step. Especially for companies that are just beginning their pricing journey, this is a very important tool.
![From Business Model Canvas to Pricing Model Canvas]()
Download the Pricing Model Canvas
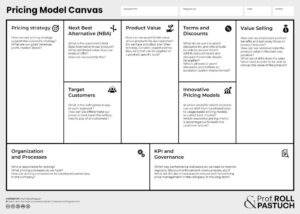
The Nine Core Topics of the Pricing Model Canvas
The following nine core topics of the Pricing Canvas help to establish target-oriented price management:
- Pricing Strategy: It is important to align the pricing strategy with the overarching corporate strategy. Depending on the strategic goals (growth vs. profitability) and the maturity of the products (lifecycle), pricing then serves as a lever for implementing the corporate strategy.
- Next Best Alternative: A comprehensive analysis of competitive products helps to understand one’s own positioning in the market. The Next Best Alternative (NBA) serves as a central concept for value-based pricing, as the customer’s willingness to pay always also depends on the price of their NBA.
- Target Customers: By conducting a sound customer segmentation and assessment of the segment potential, specific target customer segments can be identified. From a pricing perspective, it is crucial to understand the different willingness to pay of the segments and to address this through price differentiation.
- Product Value: Determining the value of the product is essential for setting a suitable price point. The focus here is on the benefits of the product from the customer’s perspective. By combining direct and indirect price inquiries (conducting market research with customers using methods like van Westendorp, Conjoint, and Garbor Granger analyses), internal assessments, and data analysis, the value provided by the product is translated into a monetary value that then becomes the decisive factor for pricing.
- Terms and Discounts: In addition to the defined list price, a performance-oriented discount and rebate system provides the opportunity for individual customer steering and purchase incentivization. It is important that terms and discounts always incentivize a type of performance from the customer and are awarded according to a clearly defined set of rules. Typical elements of terms include quantity, marketing, or process-related discounts.
- Innovative Pricing Models: In addition to traditional one-time purchase models, innovative pricing models are becoming increasingly prevalent. For example, subscription models are very common in the software industry, but pay-per-output models are also increasingly being applied in machine and plant engineering. The focus here is on determining which model is comprehensible to the customer and optimally reflects the actual added value of the product.
- Value Selling: In sales, there is a comprehensive toolbox available for convincing customers to make a purchase by specifically communicating the value of the product. Especially for innovative pricing models and product bundles consisting of hardware, software, and services, there is a shift away from traditional sales pitches towards so-called Solution Selling. Sales representatives must be trained to be able to communicate the value of the product over its entire lifecycle, including all the services offered as a complete package.
- Organization & Processes: For mature price management, it is essential for companies to incorporate a dedicated pricing department into the organization. This department is responsible for maintaining an overview of all the topics listed here and ensuring smooth processes through defined interfaces within the company.
- KPI & Governance: To ensure the long-term success of price management, responsibilities and clear guidelines for the individual processes are defined through governance. Continuous monitoring, both on the system side and in terms of content through, for example, BI reports, ensures that pricing is always aligned with current market conditions and customer needs.
Ihr direkter Ansprechpartner
Prof. Dr. Oliver Roll
Managing Partner
Mehr zum Thema
InsightsPricingSales
First awarded in 2014, we have been able to secure our place on the best list of brand...